The basic hydro-meteorological monitoring in Laos was initiated in 1998 within the Houay Pano catchment (Boithias et al., 2021). Aside from land use, water, and sediment fluxes, the observation in Laos was extended to water quality in 2011, including the fecal indicator bacterium E. coli and following a multiple-scale monitoring approach (to date: 0.6-272,155 km²) within the Mekong river basin (Boithias et al., 2022).
Details about the Houay Pano catchment can be found here and below.
Houay Pano catchment
The 60-ha Houay Pano catchment is located in northern Lao PDR, in the mountainous region of Luang Prabang.
Houay Pano stands near the village named ‘Lak Sip’, about 10 km south-east of Luang Prabang city, along the National Road 13 and 350 km North from Vientiane. Elevation in Houay Pano catchment ranges from 450 to 720 m above sea level.
The coordinates of the Houay Pano catchment are between 102°09’50’’E and 102°10’20’’E, 19°51’00’’N and 19°51’45’’N.

Climate
The climate is sub-tropical humid and is characterized by a monsoon regime with a dry season from November to May, and a rainy season from June to October. The mean annual temperature is 23.4 °C. The mean annual rainfall is 1,366 mm (CV=0.23), about 71 % (CV=0.09) of which falls during the rainy season (Boithias et al., 2021).
Precipitation data at 6 min time interval are available here, while daily precipitation data are available here. Other climate data are available here.
Hydrology
The stream flow is permanent. Currently, 3 sub-catchments are monitored (S4, S7 and S8).
Hydrological data on the catchment scale (outlet S4) are available here. Hydrological data on the plot scale are available here.
Geology
The most common rock types are gabbro, diorite, and basic rocks, such as schist, gneiss, and sandstone (Department of Geology and Mines, 1990-1991).
Soils
A detailed soil survey conducted by the Soil Survey and Land Classification Center (SSLCC) in 1996 showed that the most widespread soil groups are Acrisols, namely Alisol (FAO UNESCO system) or Ultisols (US taxonomy). They are mainly found on the slopes ranking from 8% to 50%, i.e. on most of the surveyed area.
Soil map is available here.
Vegetation and land use
The land use gradually shifted from annual crop associated to fallow periods, to teak tree plantations.
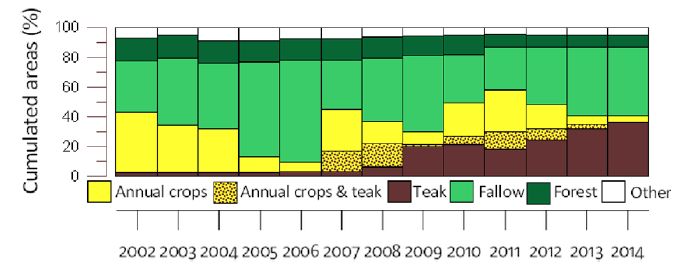
Land use data on the catchment scale are available here. Soil surface features data on the plot scale are available here.
Land use and soil erosion: a video illustration (October 2012, 09’58”).

